The Tragic Crash of Air India Express Flight 1344: A Detailed Overview
Air India Express Flight 1344, a repatriation flight under the Vande Bharat Mission, tragically crashed on August 7, 2020, in Kerala, India. The flight was returning from Dubai and attempted to land during heavy rain at Kozhikode International Airport. The Boeing 737 overshot the runway (runway excursion), resulting in the plane skidding off and breaking into two. This tragic event highlighted severe safety concerns and the dangers of flying into table-top runways, especially during adverse weather conditions.
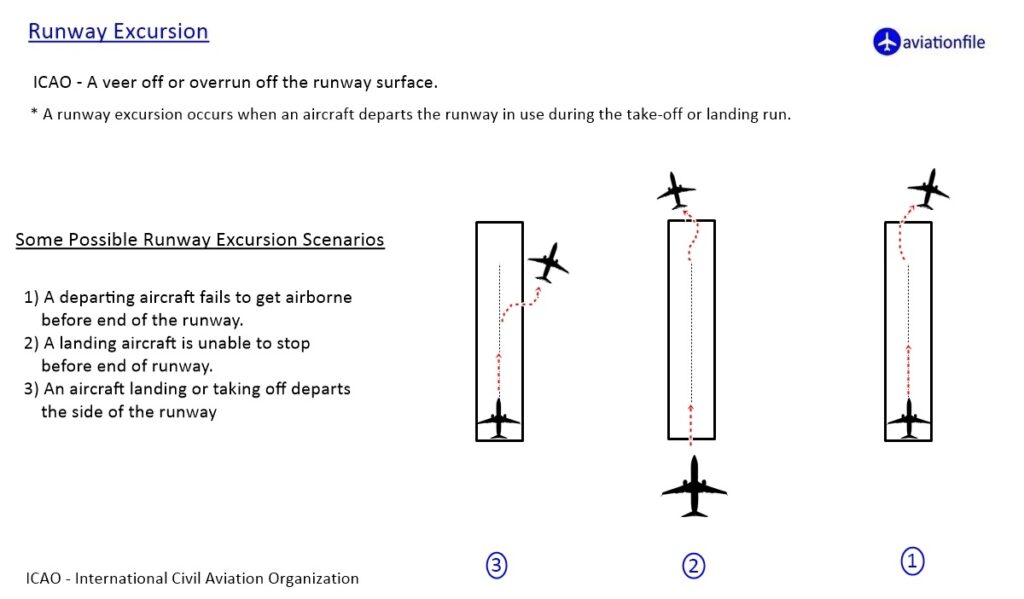
Background and Causes: The crash occurred due to a combination of factors, primarily the challenging weather and the dangerous table-top runway at Kozhikode. Investigations revealed that the pilots attempted to land twice, with the third attempt leading to the aircraft overshooting the runway. The lack of a safety area beyond the runway added to the severity of the crash, contributing to the high casualty rate.
Critical Factors
- Weather Conditions: Heavy rain and poor visibility significantly impacted the pilots’ ability to land safely.
- Runway Design: Kozhikode’s table-top runway, surrounded by a steep drop, posed a significant risk, especially during such challenging conditions.
- Pilot Actions: The decision to attempt a landing under such circumstances was questioned. Investigations suggested possible pilot error, including fatigue.
Consequences: The crash resulted in the deaths of 21 people, including both pilots, and injured many others. This tragedy sparked discussions on aviation safety, particularly regarding table-top runways in India. The incident led to calls for improved infrastructure and stricter regulations to prevent such occurrences in the future.
Safety Recommendations: Post-accident, aviation authorities emphasized the need for better pilot training for such runways and improved safety features at airports with challenging terrains. Recommendations included extending the runway safety area and enhancing runway friction tests to prevent similar incidents.
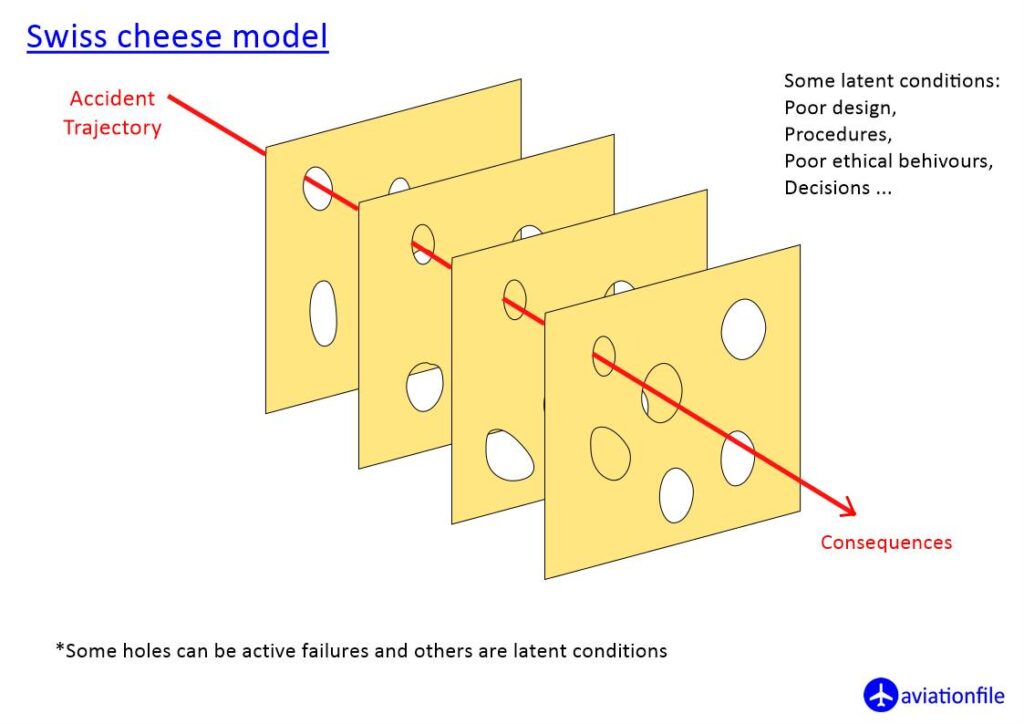
Swiss Cheese Model and the Air India Express Flight 1344 Crash
The Air India Express Flight 1344 crash can be explained using the Swiss Cheese Model, where multiple layers of defense failed. The “holes” in these layers included adverse weather (heavy rain), the challenging table-top runway, and potential pilot fatigue or error. These factors aligned, leading to the aircraft overshooting the runway and crashing. Each layer’s weaknesses, when combined, allowed the accident to occur, illustrating how complex system failures can result in disasters.
Conclusion
The Air India Express Flight 1344 crash was a tragic reminder of the importance of strict adherence to safety protocols and the need for constant evaluation and improvement of aviation infrastructure. By addressing the lessons learned from this incident, future tragedies can hopefully be avoided.


