Taking Flight Towards Sustainability in Aviation: A Deep Dive into Alternative Aircraft Engine Fuels
The aviation industry, a significant contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, is actively seeking ways to minimize its environmental impact. One crucial area of focus is the exploration of sustainability in aviation and alternative aircraft engine fuels. These fuels hold immense potential to revolutionize air travel, making it cleaner and more sustainable.
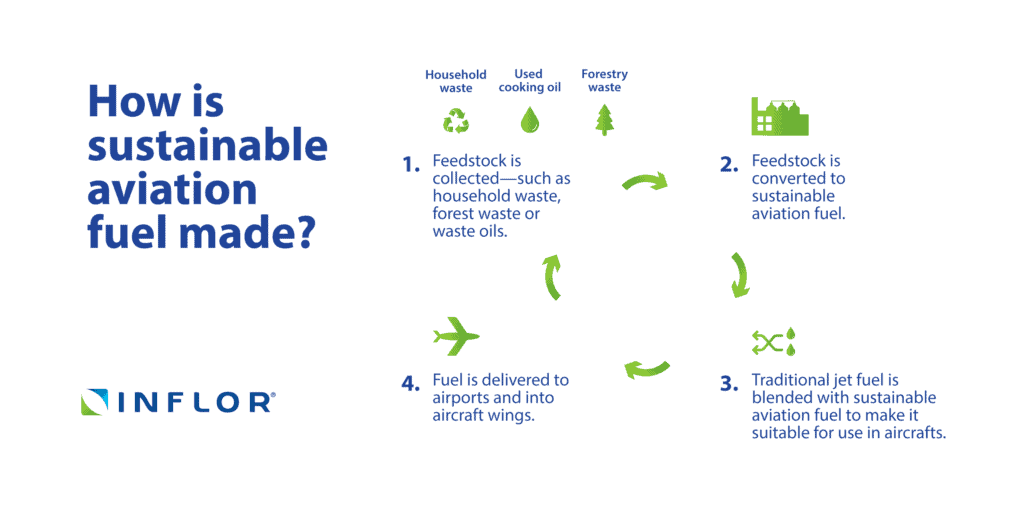
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF): A Drop-in Solution with Immediate Impact
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is currently the most viable and commercially available alternative fuel option for aircraft. Derived from renewable sources like used cooking oil, plant oils, and even captured carbon dioxide, SAF boasts similar performance characteristics to conventional jet fuel. This “drop-in” quality allows for seamless integration into existing infrastructure, making it a realistic and immediate solution for reducing the carbon footprint of air travel. Studies show that SAF can cut lifecycle emissions by up to 80% compared to traditional jet fuel.
Sustainability in Aviation
Hydrogen: A Clean-Burning Vision for the Future
Hydrogen (H2) fuel offers a promising long-term vision for sustainable aviation. When burned, hydrogen produces only water vapor as a byproduct, eliminating harmful emissions like carbon dioxide and contributing to cleaner air. Additionally, hydrogen boasts three times the energy density of traditional jet fuel per unit of weight, potentially increasing aircraft range. However, significant challenges remain. Storage and infrastructure development require substantial advancements, and aircraft engines need modifications to efficiently utilize hydrogen.
Exploring Other Alternatives: A Multi-pronged Approach
While SAF and hydrogen are frontrunners, other alternative fuels are also being explored, each with its own unique set of advantages and challenges:
- Ammonia (NH3): This fuel offers high energy density but requires modifications to existing infrastructure and engines. Additionally, concerns exist regarding its potential environmental impact during production and storage.
- Electric and Hybrid Solutions: These options are currently more suitable for shorter-range flights due to limitations in battery technology. However, advancements in battery technology hold promise for the future, potentially enabling longer-distance electric flight.
Collaboration and Innovation: Paving the Way for a Sustainable Future
The successful transition towards sustainable aviation requires a collective effort from various stakeholders. Governments need to provide incentives and invest in research and development. Fuel producers must scale up production of sustainable fuels while ensuring economic viability. Airlines need to embrace these new technologies and adapt their operations accordingly. Finally, aircraft manufacturers must play a crucial role in developing engines optimized for alternative fuels.
By working together and fostering innovation, these stakeholders can pave the way for a cleaner and more sustainable future for air travel, ensuring the skies remain accessible for generations to come.
References and Further Reading:
- Department of Energy – Sustainable Aviation Fuels: https://www.energy.gov/eere/bioenergy/sustainable-aviation-fuels
- The European Commission – Alternative fuels used for aviation: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/news/en/press-room/20230911IPR04913/70-of-jet-fuels-at-eu-airports-will-have-to-be-green-by-2050
- Simple Flying – 5 Alternative Fuel Technologies That Could Define Aviation’s Race To Net-Zero: https://simpleflying.com/tag/jet-fuel/
- Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) – https://inflor.com/blog/benefits-of-sustainable-aviation-fuel/



