What is “SQUAWK” code ?
The word “squawk” means “to utter a loud, harsh cry, as a duck or other fowl when frightened.”. However, the word “Squawk” also widely used within the aviation community, The meaning of the word is slightly different. Let’s examine what Squawk code means in aviation.
The Squawk Code in aviation, is a four-digit octal number Mod-3 code defined in the transponder box by the pilot in line with the instruction of the air traffic control officer. With the help of this code, various data about the flight becomes visual on the ATC radar screen.

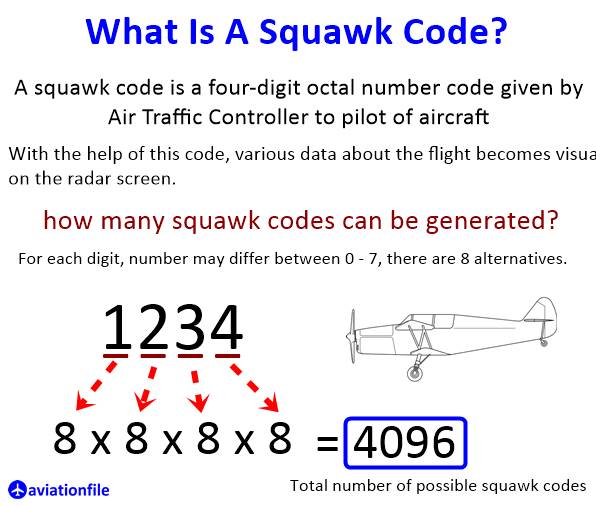
How Many Squawk Codes
The Squawk Code is written according to the octal number system and therefore consists of numbers from 0 to 7. Considering that there can be 8 alternatives in each digit, there are 8x8x8x8 = 4,096 different squawk codes.
We can summarize an example usage with a sample pilot-controller communication as follows;
Pilot: ABA Delivery, XYZ123 request ATC clearance.
ATC: XYZ123, ABA Delivery ATC clears you to destination EDDD via flight plan route, climb FL 240, squawk 2561.
Pilot: Reads back the ATC instructions…
In this example, with the “squawk 2561” instruction, the 4-digit code requested from the pilot is set to the relevant place on the plane.
Thanks to this code set on the aircraft, information such as speed, altitude, flight number of the aircraft during the flight become visible on the radar screen. In this way, Controllers can provide separation between aircraft and a safe and secure air traffic flow is ensured.
Emergency “Squawk” Codes
Besides, the squawk code is also used in emergencies.
There are three basic emergency codes that are familiar to almost anyone with an amateur aviation interest:
7500 Hijacking (The plane was hijacked)
7600 Radio Failure
7700 General Emergency (General emergency. Aircraft malfunctions, medical emergency, etc.)
When pilots set these codes on their aircraft when necessary, they inform the air traffic control center about the emergency they are in.

Resources:
https://www.dictionary.com/browse/squawk
ICAO doc4444



