Point of No Return (PNR) in Aviation: A Crucial Decision-Making Point
In the realm of aviation, the Point of No Return (PNR) marks a critical juncture during a flight, signifying the point beyond which an aircraft can no longer safely return to its origin due to fuel constraints. This crucial decision-making point is determined by a combination of factors, including the aircraft’s fuel capacity, prevailing wind conditions, and the distance to the destination and alternate airports.
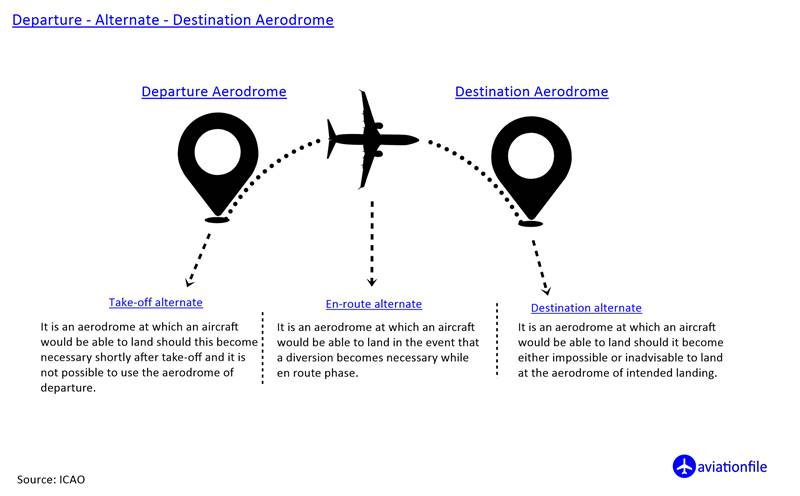
Beyond the PNR: Continuing Towards the Destination
Once an aircraft surpasses the PNR, returning to the departure point becomes an impractical and potentially hazardous endeavor. The aircraft must, therefore, continue its journey towards the intended destination or divert to an alternate airport, ensuring the safety of the passengers and crew.
Factors Influencing PNR Calculation
The precise location of the PNR varies depending on several factors, including:
- Fuel Consumption: The aircraft’s fuel consumption rate plays a significant role in determining the PNR. Higher fuel consumption rates necessitate an earlier PNR to ensure sufficient fuel reserves for the return trip.
- Wind Conditions: Prevailing wind conditions can significantly impact the PNR calculation. Tailwinds, which push the aircraft along, can extend the PNR, while headwinds, which hinder progress, necessitate an earlier PNR.
- Distance to Destination and Alternate Airports: The distance to the destination and potential alternate airports also influences the PNR. Shorter distances allow for a later PNR, while longer distances require an earlier PNR to provide adequate fuel reserves for contingencies.
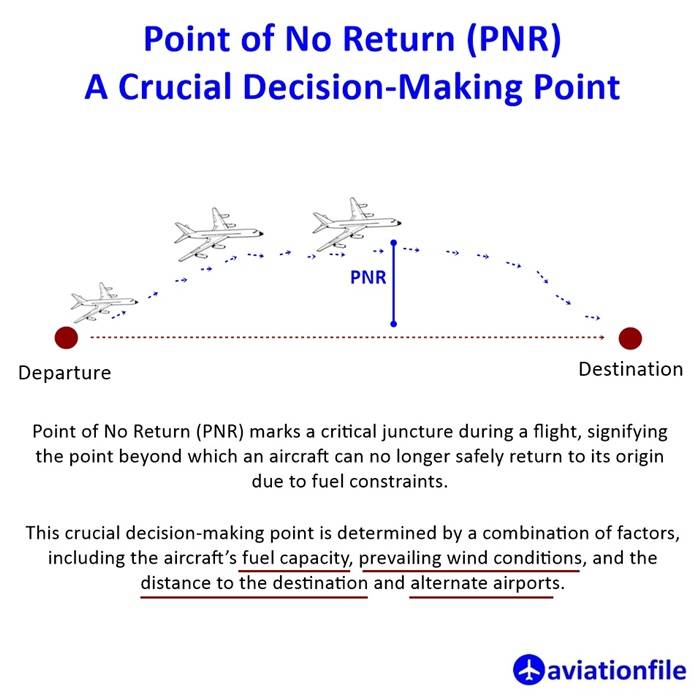
PNR: A Crucial Safety Measure
The PNR serves as a vital safety measure in aviation, ensuring that aircraft operate within their fuel limitations and have adequate reserves for potential diversions. By carefully calculating and adhering to the PNR, pilots can make informed decisions that prioritize the safety of all onboard.
References:
- A Simplified Guide for Pilots. https://skybrary.aero/articles/point-no-return-pnr
- “Airplane Flying Handbook – Chapter 11: Flight Planning.” https://skybrary.aero/articles/point-no-return-pnr
- https://skybrary.aero/articles/point-no-return-pnr
- Quora. https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-point-of-no-return



